The RMM Explained
Risk Management Benchmarking and Progress
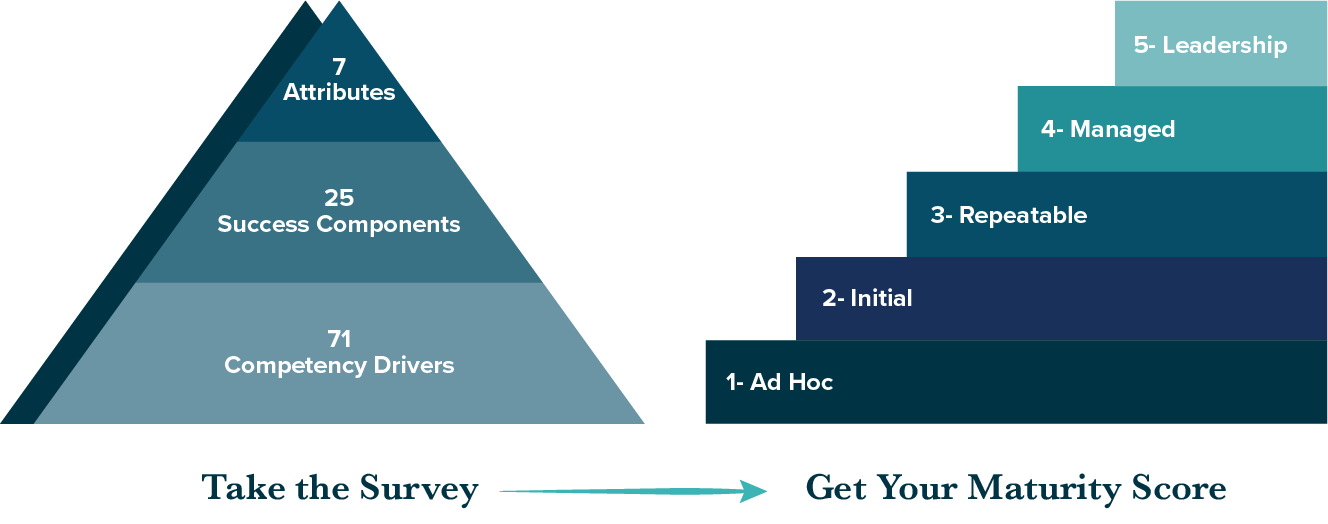
The Risk Maturity Model (RMM) outlines key indicators and activities that comprise a sustainable, repeatable and mature enterprise risk management (ERM) program. Taking the risk maturity self-assessment, organizations benchmark how in line their current risk management practices are with the RMM indicators. Once completed, each organization is provided with a maturity score for their program, starting at the earliest stage and lowest risk maturity level, Ad-Hoc (Level 1), and progressing to the most advanced, risk maturity level, Leadership (Level 5). The following will outline each component of the RMM’s risk maturity assessment, how each gets scored, and the results of taking the assessment.
Seven Attributes
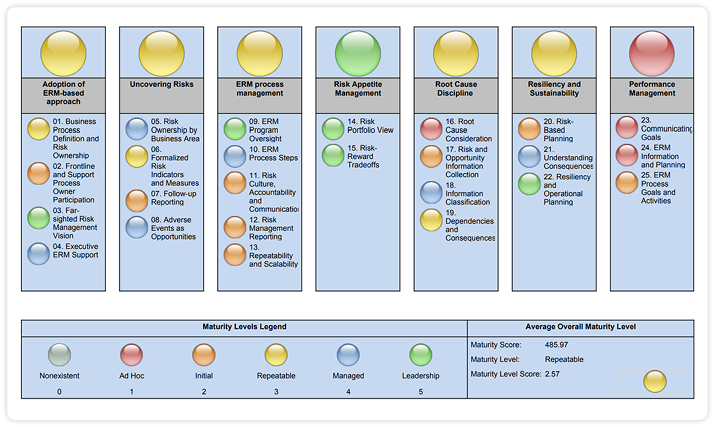
The Risk Maturity Model (RMM) identifies seven key attributes for effective enterprise risk management. These attributes cover the planning and governance of an ERM program, as well as the execution of assessments, and aggregation and analysis of risk information.
The seven attributes, or components of a best practice ERM program, are as follows:
-
Adoption of ERM-Based Process
This attribute measures the organization’s risk culture, and considers the degree of executive or board-level support for enterprise risk management.
-
ERM Process Management
This attribute measures the extent to which the organization has adopted an ERM methodology throughout its culture and business decisions, and how well the risk management program follows best practice steps to identify, assess, evaluate, mitigate, and monitor risks.
-
Risk Appetite Management
This attribute evaluates the level of awareness around risk-reward trade-offs, accountability for risk, defining risk tolerances, and whether the organization is effective in closing the gap between potential and actual risk.
-
Root Cause Discipline
This attribute assesses the extent to which an organization identifies risk by source, or root cause, versus the symptoms and outcomes they produce. Focusing on the root cause of a risk and classifying them accordingly will strengthen response and mitigation efforts.
-
Uncovering Risks
This attribute measures the quality and coverage of your risk assessments. It examines the method of collecting risk information, the risk assessment process, and whether enterprise-wide trends and correlations can be uncovered from the risk information.
-
Performance Management
This attribute determines the degree to which an organization executes on its visions and strategy. It evaluates the strength in planning, communicating, and measuring core enterprise goals with a risk-based process, and the extent to which progress deviates from expectations.
-
Business Resiliency and Sustainability
This attribute evaluates the extent to which business continuity, operational planning, and other sustainability activities are approached with a risk-based methodology.
Competency Drivers & Indicators
Each attribute includes a set of competency drivers which outline the key readiness indicators (or activities) involved in achieving each driver. These driver/indicator pairs cover the entire risk management process including administration, outreach, data collection and aggregation, and analysis of risk information. Below is a sample of the 25 competency drivers and indicator pairings which comprise the RMM’s risk maturity assessment:
Executive ERM Support
- Are risk priorities and progress reported to the board of directors or senior leadership?
- Are risk assessments required for new initiatives (i.e. projects, operational changes, vendor on-boarding, etc.)?
- Is risk management education and comprehension considered in employee performance reviews?
Information Classification
- Is there a standardized process or classification model for identifying risk?
- Do business areas identify organizational goals and track progress towards achievement?
- Are risks identified by root-cause or their source?
Business Process Definition and Risk Ownership
- Do business areas identify process-related risks?
- Do process owners manage their risks, threats, and opportunities within regular planning and strategizing?
- Are all risks, threats and opportunities communicated and acted upon in a timely manner?
Scoring Methodology
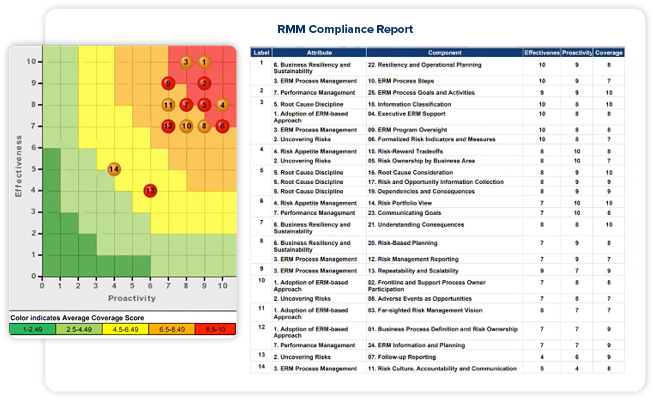
All competency drivers are scored on a scale of 1-10 for each of the three following assessment dimensions:
-
Effectiveness
Measures the frequency and effectiveness of key risk management activities. (i.e. Are assessments ad-hoc or completed annually? Are high risks reviewed at least quarterly?)
-
Proactivity
Measures the nature of risk management, whether it is proactive or reactive. (i.e. Does the organization wait until an adverse event occurs to mitigate risk or are future scenarios planned for?)
-
Coverage
Measures the breadth and depth of risk management within the organization. (i.e. Does responsibility span across all departments and all vertical levels of the organization?)
Once completed, a maturity score is provided for each driver as well as an overall maturity score for the entire risk management program. Scoring is based on a 5-level scale, with Level 1 indicating the lowest risk maturity and a Level 5 representing the highest maturity. With a maturity score for each factor, organizations can prioritize time and resources on improving the weakest areas of their risk management process while retaining the strongest practices.
Based on proven best practice activities, organizations who implement the RMM indicators, are able to create and experience the benefit of effective risk management. Aiding organizations in bridging the gaps and maturing their risk management programs, LogicManager provides a number of resources and methods of assistance.
How to Take the RMM Risk Maturity Assessment
Typically, organizations take two routes when completing the RMM’s risk management maturity assessment: Either a single individual completes the assessment on behalf of the ERM program (someone central to the risk management program and practices), or several individuals take the assessment and aggregate the scores from multiple assessors involved in different areas of the ERM program.
There are two versions of the RMM: the standard version is designed to be taken by a leader in the organization who’s looking to get an overall sense of their ERM maturity. The second version, the RMM for the Frontline, is designed to be taken by employees directly carrying out the day-to-day operations and processes that power the organization. The difference between the standard RMM and the RMM for the Frontline is the competency drivers (the former will be asked questions about more high-level enterprise concerns, while the latter will examine areas they’re more closely related to). While one method may be better suited than the other depending on each ERM program’s structure, both produce meaningful maturity scores and reports to leverage when improving an ERM program.
To take the free, online RMM assessment, visit this link! Once completed, the assessment provides a personalized report of your scores including a comparison between your report and the success factor guidelines. This helps you identify and prioritize gaps, as well as develop an action plan to advance your risk management program. The assessment requires no prior experience, takes about 30 minutes to complete and is completed through an online, easy-to-use assessment wizard. Click here to take the RMM assessment!
If you have any questions about the RMM assessment or would like to set up a meeting to discuss your results, please email communications@logicmanager.com.
- For more information on the Risk Maturity Model (RMM) visit the RMM Resource Center.
- For further guidance on effective enterprise risk management practices, visit the complimentary ERM Resource & Knowledge Center.